Clockwise Unit Circle This will be studied in the next exercise Exercise 1 1 2 1 1 2 The following diagram is a unit circle with 24 24 points equally space points plotted on the circle Since the circumference of the circle is 2 2 units the increment between two consecutive points on the circle is 2 24 12 2 24 12
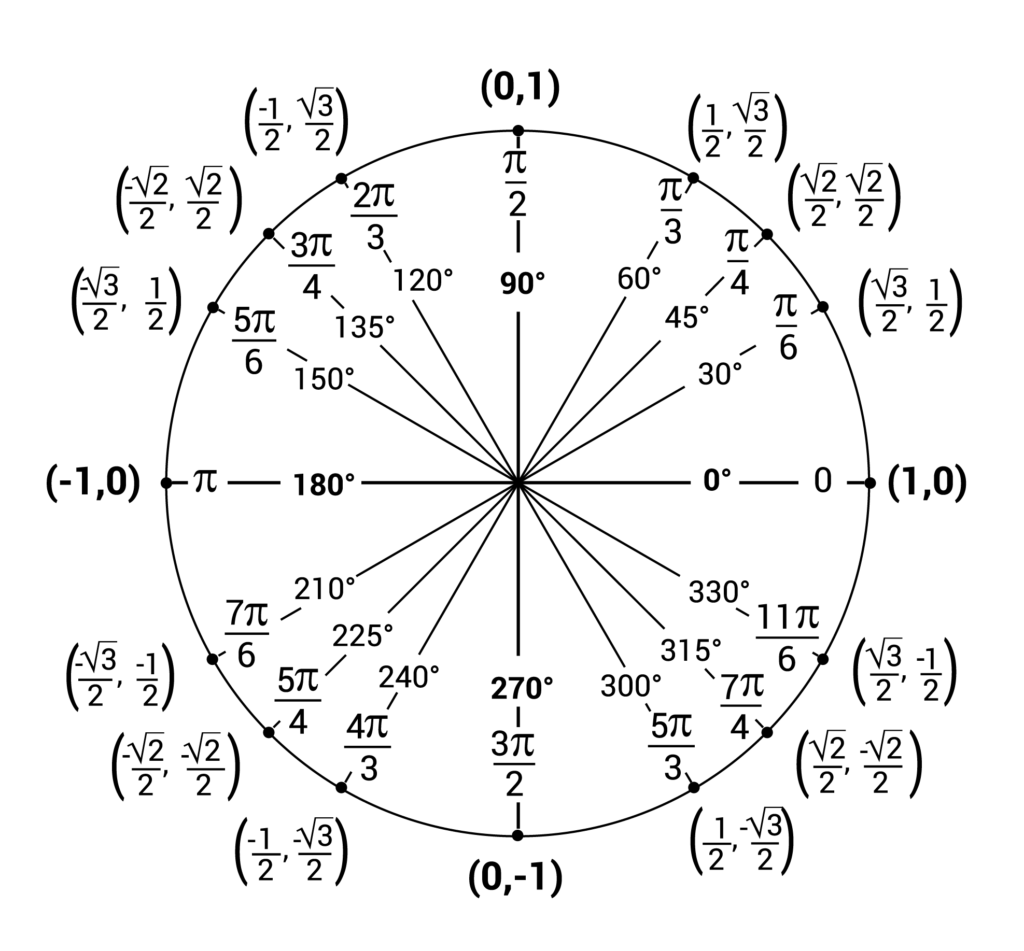
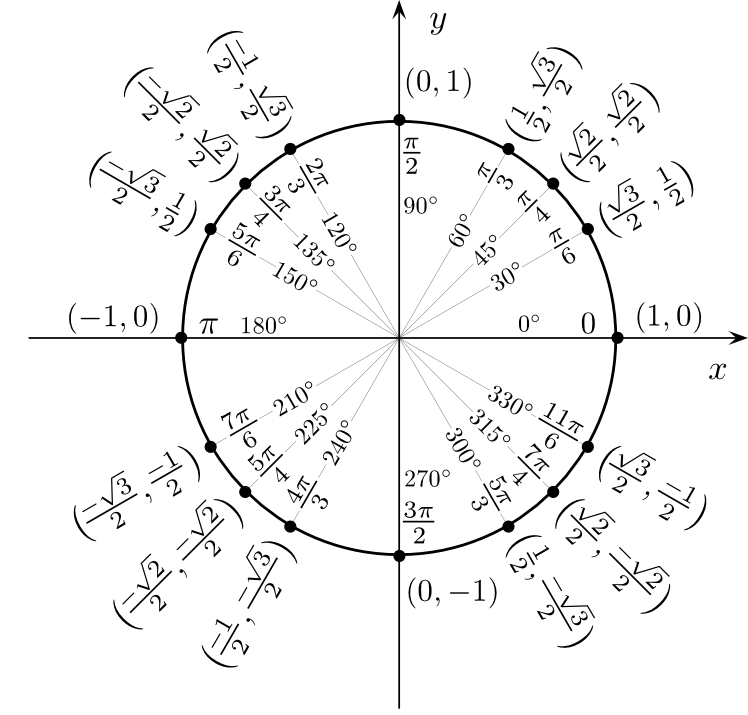
The unit circle is a circle of radius 1 unit that is centered on the origin of the coordinate plane The unit circle is fundamentally related to concepts in trigonometry The trigonometric functions can be defined in terms of the unit circle and in doing so the domain of these functions is extended to all real numbers Pythagoras Pythagoras Theorem says that for a right angled triangle the square of the long side equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides x 2 y 2 1 2 But 1 2 is just 1 so x 2 y 2 1 equation of the unit circle Also since x cos and y sin we get cos 2 sin 2 1 a useful identity Important Angles 30 45 and 60 You should try to remember sin
Clockwise Unit Circle

Clockwise Unit Circle
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/56/48/98/564898768ea350d1c3ac01edb03fea10.jpg
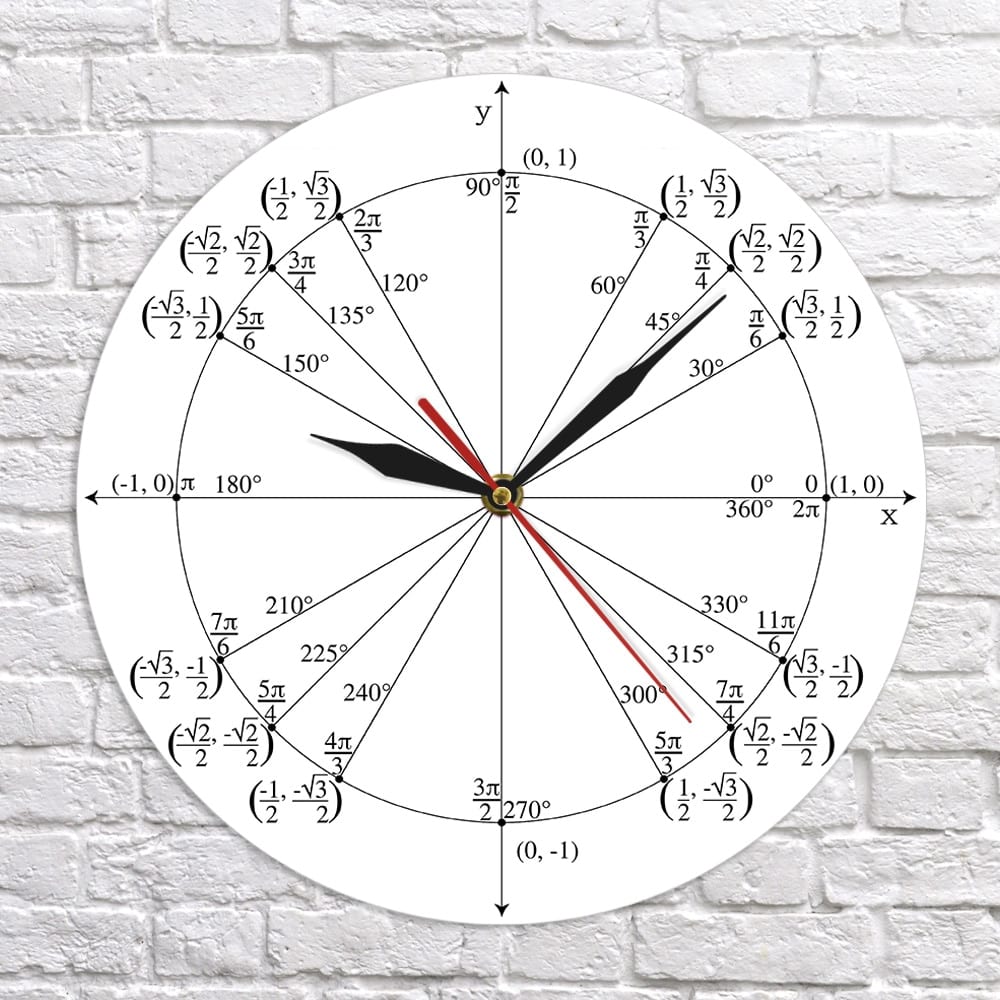
Mathematical Trigonometric Wall Clock
https://chemicalacademy.shop/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/6231-bdf5ac.jpg
Unit Circle
https://www.learnalberta.ca/content/memg/Division04/Unit Circle/DegRad.jpg
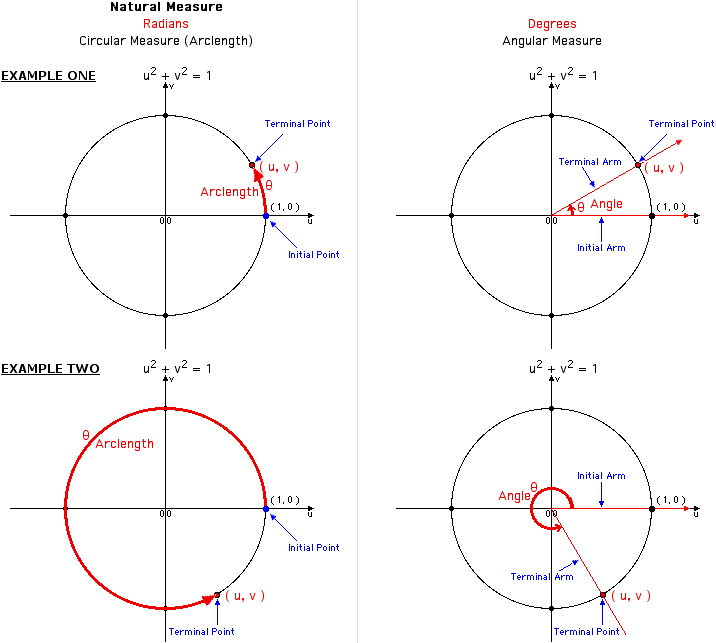
In the unit circle we say the angle s measure is 1 radian provided that the angle intercepts an arc of the circle that is 1 unit in length as pictured in Figure 2 2 4 Note particularly that an angle measuring 1 radian intercepts an arc of the same length as the circle s radius The Cosine and Sine Functions as Coordinates on the Unit Circle In Section 10 1 we introduced circular motion and derived a formula which describes the linear velocity of an object moving on a circular path at a constant angular velocity One of the goals of this section is describe the position of such an object To that end consider an angle theta in standard position and let P
Defining Sine and Cosine Functions from the Unit Circle The sine function relates a real number t t to the y coordinate of the point where the corresponding angle intercepts the unit circle More precisely the sine of an angle t t equals the y value of the endpoint on the unit circle of an arc of length t t In Figure 2 the sine is equal to When measuring angles on a circle unless otherwise directed we measure angles in standard position starting at the positive horizontal axis with a counterclockwise rotation Measuring Angles in Degrees A degree is a unit of measurement of an angle One rotation around a circle is equal to 360 degrees
More picture related to Clockwise Unit Circle
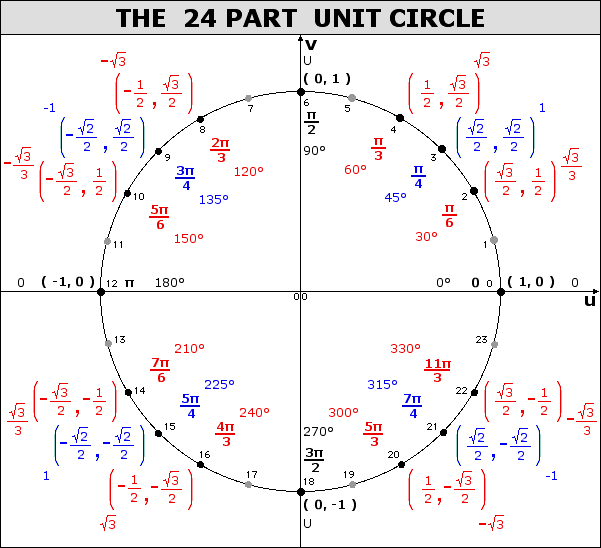
The Eight Part Unit Circle
https://www.learnalberta.ca/content/memg/Division04/Unit Circle/gfx/UC24.gif
Unit Circles And Standard Position Video Practice Questions
https://cdn-academy.pressidium.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Unit-circle-1024x951.png

The Unit Circle Algebra 2 Trig Math Lessons
https://mathsux.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/screen-shot-2020-10-28-at-4.49.05-pm.png?w=1024&is-pending-load=1
Always remember to measure the angle from the positive portion of the x axis Figure 2 3 1 1 2 3 1 1 Knowing the first quadrant well is the key to knowing the entire unit circle Every other point on the unit circle can be found using logic and this quadrant so there is no need to memorize the whole circle What is a unit circle A unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1 unit radius In most cases it is centered at the point 0 0 0 0 the origin of the coordinate system The unit circle is a really useful concept when learning trigonometry and angle conversion
3 Answers Sorted by 1 A parametrization is not unique Suppose you parametrize the circle as r cost r sint r cos t r sin t with t 0 2 t 0 2 Then when t 0 t 0 you begin at the point r 0 r 0 Then t t increases until t 2 t 2 and you arrive to the point 0 r 0 r so you are going counterclockwise Angles in Trigonometry The Unit Circle Degrees Radians and Co Terminal Angles More Practice Angles in Trigonometry Even though the word trigonometry is derived from the word triangle you ll see a lot of circles when you work with Trig Angle measurements start at 0 on the positive x axis and go counter clockwise around the

Unit Circle
http://s1.thingpic.com/images/WG/AThAAcUNiRz23itWMu36.gif
Trigonometry Worked Examples
https://www.math.toronto.edu/preparing-for-calculus/8_trigonometry/images/unit_circle_angles.png
Clockwise Unit Circle - When measuring angles on a circle unless otherwise directed we measure angles in standard position starting at the positive horizontal axis with a counterclockwise rotation Measuring Angles in Degrees A degree is a unit of measurement of an angle One rotation around a circle is equal to 360 degrees